Acyclovir for Injection, USP
QUICK DETAILS:
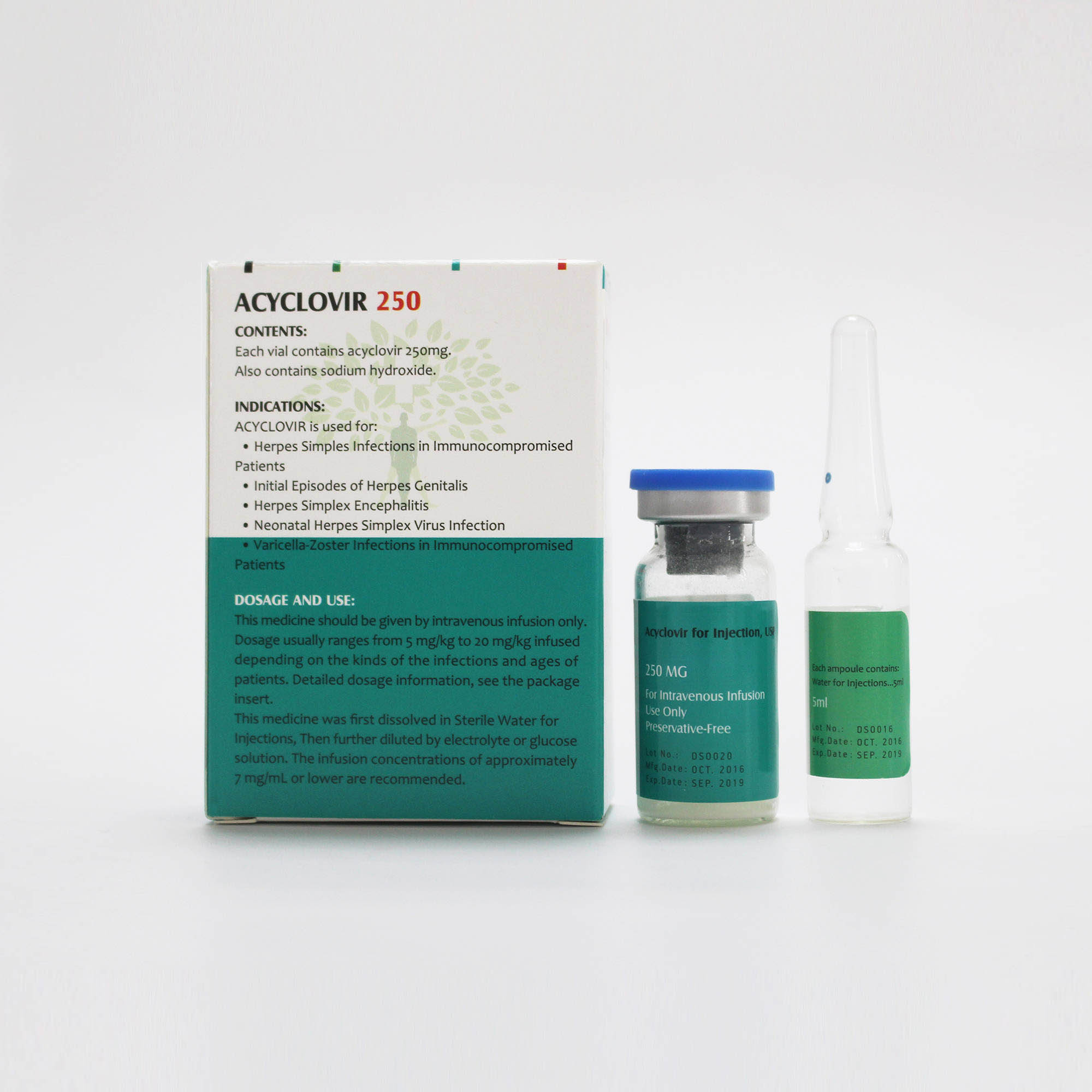
ACYCLOVIR Content:
• Each vial of this medicine contains Acyclovir 250mg as the active ingredient.
• The other ingredients are sodium hydroxide.
ACYCLOVIR Character:
ACYCLOVIR is a sterile white lyophilized powder.
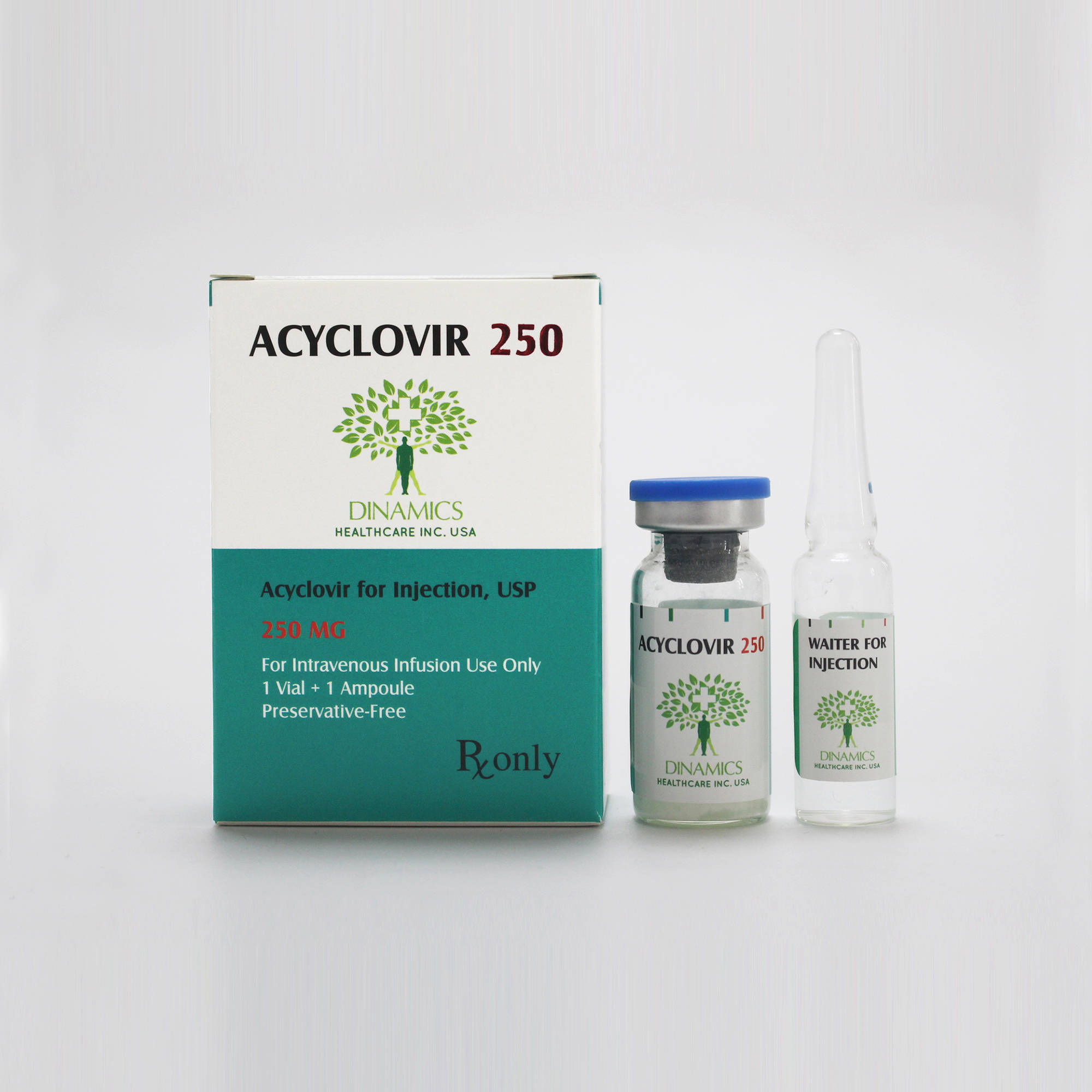
ACYCLOVIR Pack:
ACYCLOVIR comes in a clear glass vial fitted with a rubber cap and metal seal.
The pack contains a vial containing 250 mg acyclovir, also contains an ampoule containing 5 ml sterile water for injections.
DESCRIPTION
1.What ACYCLOVIR is and what it is used for
This medicine contains the active substance acyclovir, a synthetic nucleoside analog active against herpesviruses. It is a sterile lyophilized powder for intravenous administration only.
ACYCLOVIR is used for:
Herpes Simplex Infections in Immunocompromised Patients: Acyclovir for Injection is indicated for the treatment of initial and recurrent mucosal and cutaneous herpes simplex (HSV-1 and HSV-2) in immunocompromised patients.
Initial Episodes of Herpes Genitalis: Acyclovir for Injection is indicated for the treatment of severe initial clinical episodes of herpes genitalis in immunocompetent patients.
Herpes Simplex Encephalitis: Acyclovir for Injection is indicated for the treatment of herpes simplex encephalitis.
Neonatal Herpes Simplex Virus Infection: Acyclovir for Injection is indicated for the treatment of neonatal herpes infections.
Varicella-Zoster Infections in Immunocompromised Patients: Acyclovir for Injection is indicated for the treatment of varicella-zoster (shingles) infections in immunocompromised patients.
2. What you need to know before you take ACYCLOVIR
Do not use ACYCLOVIR if:
• You are allergic (hypersensitive) to acyclovir or valacyclovir or any of the other ingredients of this medication.
If you are not sure, talk to your doctor or pharmacist before using it.
Warnings and Precautions
Warnings
Acyclovir for Injection is intended for intravenous infusion only, and should not be administered topically, intramuscularly, orally, subcutaneously, or in the eye. Intravenous infusions must be given over a period of at least 1 hour to reduce the risk of renal tubular damage.
Renal failure, in some cases resulting in death, has been observed with acyclovir therapy. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura/hemolytic uremic syndrome (TTP/HUS), which has resulted in death, has occurred in immunocompromised patients receiving acyclovir therapy.
Precautions
General:
Precipitation of acyclovir crystals in renal tubules can occur if the maximum solubility of free acyclovir (2.5 mg/mL at 37°C in water) is exceeded or if the drug is administered by bolus injection. Ensuing renal tubular damage can produce acute renal failure.
Abnormal renal function (decreased creatinine clearance) can occur as a result of acyclovir administration and depends on the state of the patient’s hydration, other treatments, and the rate of drug administration. Concomitant use of other nephrotoxic drugs, pre-existing renal disease, and dehydration make further renal impairment with acyclovir more likely. Administration of ACYCLOVIR by intravenous infusion must be accompanied by adequate hydration.
When dosage adjustments are required, they should be based on estimated creatinine clearance.
Approximately 1% of patients receiving intravenous acyclovir have manifested encephalopathic changes characterized by either lethargy, obtundation, tremors, confusion, hallucinations, agitation, seizures, or coma. ACYCLOVIR should be used with caution in those patients who have underlying neurologic abnormalities and those with serious renal, hepatic, or electrolyte abnormalities, or significant hypoxia.
Using other medicines
Coadministration of probenecid with acyclovir has been shown to increase the mean half-life and the area under the concentration-time curve. Urinary excretion and renal clearance were correspondingly reduced.
Please tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking or have recently taken any other medicines. This includes medicines obtained without prescription, including herbal medicines.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before using any medicine.
DIRECTION
1.How to take ACYCLOVIR
Dosage:
Herpes Simplex Infections: Mucosal and Cutaneous Herpes Simplex (HSV-1 and HSV-2) Infections in Immunocompromised Patients:
Adults and Adolescents (12 years of age and older): 5 mg/kg infused at a constant rate over 1 hour, every 8 hours for 7 days.
Pediatrics (Under 12 years of age): 10 mg/kg infused at a constant rate over 1 hour, every 8 hours for 7 days.
Severe Initial Clinical Episodes of Herpes Genitalis:
Adults and Adolescents (12 years of age and older): 5 mg/kg infused at a constant rate over 1 hour, every 8 hours for 5 days.
Herpes Simplex Encephalitis:
Adults and Adolescents (12 years of age and older): 10 mg/kg infused at a constant rate over 1 hour, every 8 hours for 10 days.
Pediatrics (3 months to 12 years of age): 20 mg/kg infused at a constant rate over 1 hour, every 8 hours for 10 days.
Neonatal Herpes Simplex Virus Infections (Birth to 3 months): 10 mg/kg infused at a constant rate over 1 hour, every 8 hours for 10 days. In neonatal herpes simplex infections, doses of 15 mg/kg or 20 mg/kg (infused at a constant rate over 1 hour every 8 hours) have been used; the safety and efficacy of these doses are not known.
Varicella Zoster Infections: Zoster in Immunocompromised Patients: Adults and Adolescents (12 years of age and older): 10 mg/kg infused at aconstant rate over 1 hour, every 8 hours for 7 days.
Pediatrics (Under 12 years of age): 20 mg/kg infused at a constant rate over 1 hour, every 8 hours for 7 days.
Obese Patients: Obese patients should be dosed at the recommended adult dose using Ideal Body Weight.
Patients with Acute or Chronic Renal Impairment:Refer to above for recommended doses.
Hemodialysis: For patients who require dialysis, the mean plasma half-life of acyclovir during hemodialysis is approximately 5 hours. This results in a 60% decrease in plasma concentrations following a 6-hour dialysis period.Therefore, the patient’s dosing schedule should be adjusted so that an additional dose is administered after each dialysis.Peritoneal Dialysis: No supplemental dose appears to be necessary after adjustment of the dosing interval.
Method of Preparation: The contents of the vial should be dissolved in 5 mL Sterile Water for Injection attached, so the resulting solution contains 50 mg acyclovir per mL. Shake the vial well to assure complete dissolution before measuring and transferring each individual dose. The reconstituted solution should be used within 12 hours. Refrigeration of reconstituted solution may result in the formation of a precipitate which will redissolve at room temperature.
Administration: The calculated dose should then be removed and added to any appropriate intravenous solution at a volume selected for administration during each 1-hour infusion. Infusion concentrations of approximately 7 mg/mL or lower are recommended. In clinical studies, the average 70-kg adult received between 60 and 150 mL of fluid per dose. Higher concentrations (e.g., 10 mg/mL) may produce phlebitis or inflammation at the injection site upon inadvertent extravasation. Standard, commercially available electrolyte and glucose solutions are suitable for intravenous administration; biologic or colloidal fluids (e.g., blood products, protein solutions, etc.) are not recommended.
Once diluted for administration, each dose should be used within 24 hours.
2. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
General: Anaphylaxis, angioedema, fatigue, fever, headache, pain, peripheral edema.
Digestive: Abdominal pain, diarrhea, gastrointestinal distress, nausea.
Cardiovascular: Hypotension.
Hematologic and Lymphatic: Disseminated intravascular coagulation, hemolysis, leukocytoclastic vasculitis, leukopenia, lymphadenopathy. Hepatobiliary Tract and Pancreas: Elevated liver function tests, hepatitis, hyperbilirubinemia, jaundice.
Musculoskeletal: Myalgia.
Nervous: Aggressive behavior, agitation, ataxia, coma, confusion, delirium, dizziness, dysarthria, encephalopathy, hallucinations, obtundation, paresthesia, psychosis, seizure, somnolence, tremor. These symptoms may be marked, particularly in older adults.
Skin: Alopecia, erythema multiforme, photosensitive rash, pruritus, rash, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, urticaria. Severe local inflammatory reactions, including tissue necrosis, have occurred following infusion of ACYCLOVIR into extravascular tissues.
Special Senses: Visual abnormalities.
Urogenital: Renal failure, elevated blood urea nitrogen, elevated creatinine.
INGREDIENTS
Contents of the pack and other information
What ACYCLOVIR contains
• Each vial of this medicine contains Acyclovir 250mg as the active ingredient.
• The other ingredients are sodium hydroxide.
What ACYCLOVIR looks like and contents of the pack
ACYCLOVIR is a sterile white lyophilized powder which comes in a clear glass vial fitted with a rubber cap and metal seal.
The pack contains a vial containing 250 mg acyclovir, also contains an ampoule containing 5 ml sterile water for injections.
STORE
How to store ACYCLOVIR
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
Do not use after the expiry date ‘EXP’ shown on the container. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
Store below 25°C. Protect from light.
Once the medicine has been mixed with provided solvent, the solution should be used straight away. Any unused liquid should be disposed of safely.