Esomeprazole for injection
QUICK DETAILS:
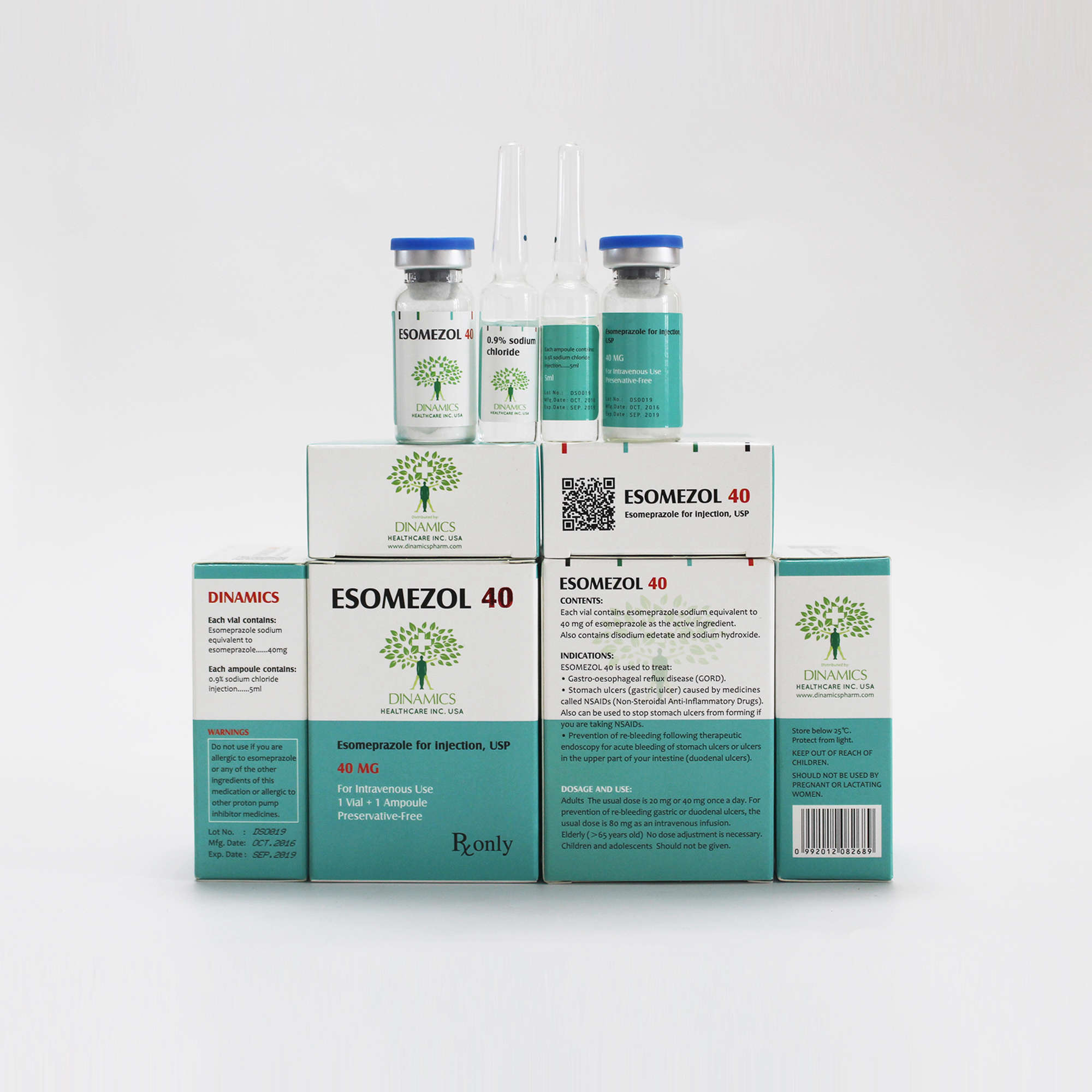
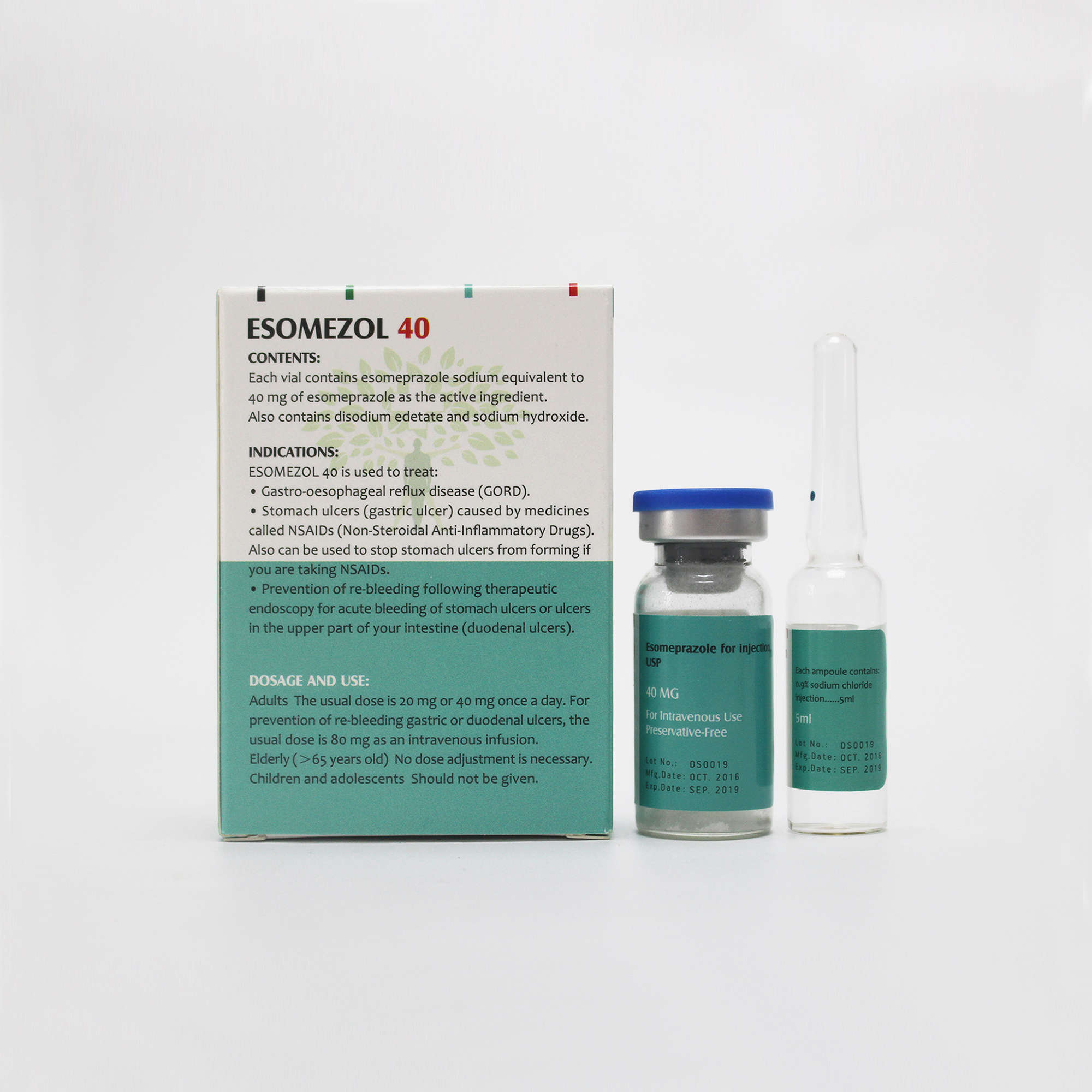
ESOMEZOL 40 Contents:
•Each vial of this medicine contains Esomeprazole (as sodium) 40mg as the active ingredient.
•The other ingredients are disodium edetate, sodium hydroxide for pH adjustment.
ESOMEZOL 40 Character:
ESOMEZOL 40 is a white or almost white lyophilized powder which comes in a clear glass vial fitted with a rubber cap and metal seal.
ESOMEZOL 40 Pack:
The pack contains a vial containing 40 mg esomeprazole, also contains an ampoule containing 5 ml 0.9% sodium chloride injections.
DESCRIPTION
1. What ESOMEZOL 40 is and what it is used for
This medicine contains the active substance esomeprazole. It belongs to a group of medicines called ‘proton pump inhibitors’. They work by reducing the amount of acid that your stomach produces.
ESOMEZOL 40 is used for the short-term treatment of certain conditions, when you are unable to have treatment by mouth.
It is used to treat:
•Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD). This is where acid from the stomach escapes into the gullet (the tube which connects your throat to your stomach) causing pain, inflammation and heartburn.
•Stomach ulcers (gastric ulcer) caused by medicines called NSAIDs
(Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs). Esomeprazole can also be used to stop stomach ulcers from forming if you are taking NSAIDs.
• Prevention of re-bleeding following therapeutic endoscopy for acute bleeding of stomach ulcers or ulcers in the upper part of your intestine (duodenal ulcers).
2. What you need to know before you take ESOMEZOL 40
You must not be given ESOMEZOL 40 if:
•You are allergic (hypersensitive) to esomeprazole or any of the other ingredients of this medication.
•You are allergic to other proton pump inhibitor medicines (e.g. pantoprazole, lansoprazole, rabeprazole, omeprazole).
•You are taking a medicine containing nelfinavir (used for HIV infection).
•If you are not sure, talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before you are given this medicine.
Take special care with ESOMEZOL 40
Check with your doctor or nurse before you are given Esomeprazole if:
•You have severe liver problems.
•You have severe kidney problems.
•You have ever had a skin reaction after treatment with a medicine similar to esomeprazole that reduces stomach acid.
If you get a rash on your skin, especially in areas exposed to the sun tell your doctor as soon as you can, as you may need to stop your treatment with esomeprazole. Remember to also mention any other ill-effects like pain in your joints.
Esomeprazole may hide the symptoms of other diseases. Therefore, if any of the following happen to you before you are given Esomeprazole or after you are given it, talk to your doctor straight away:
•You lose a lot of weight for no reason and have problems swallowing.
•You get stomach pain or indigestion.
•You begin to vomit food or blood.
•You pass black stools (blood-stained faeces).
Taking a proton pump inhibitor like Esomeprazole, especially over a period of more than one year, may slightly increase your risk of fracture in the hip, wrist or spine. Tell your doctor if you have osteoporosis or if you are taking corticosteroids (which can increase the risk of osteoporosis).
Using other medicines
Please tell your doctor or nurse if you are taking, or have recently taken, any other medicines including medicines that you buy without a prescription. This is because Esomeprazole can affect the way some medicines work and some medicines can have an effect on Esomeprazole .
You must not be given Esomeprazole if you are taking a medicine containing nelfinavir (used to treat HIV infection).
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking any of the following medicines:
•Atazanavir (used to treat HIV).
•Ketoconazole, itraconazole or voriconazole (used to treat infections caused by a fungus).
•Citalopram, imipramine or clomipramine (used to treat depression).
•Diazepam (used to treat anxiety, relax muscles or in epilepsy).
•Phenytoin (used in epilepsy). If you are taking phenytoin, your doctor will need to monitor you when you start or stop having Esomeprazole.
•Medicines that are used to thin your blood, such as warfarin. Your doctor may need to monitor you when you start or stop having Esomeprazole.
•Cisapride (used for indigestion and heartburn).
•Clopidogrel (used to prevent blood clots)
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Before you are given Esomeprazole, tell your doctor if you are pregnant or trying to get pregnant. Your doctor will decide whether you can be given Esomeprazole during this time.
It is not known if esomeprazole passes into breast milk. Therefore, you should not be given Esomeprazole if you are breastfeeding.
Driving and using machines
Esomeprazole is not likely to affect your ability to drive or use any tools or machines.
DIRECTION
1.How to take ESOMEZOL 40
Esomeprazole will be given to you by a doctor or nurse. Your doctor will decide how much you need. Please tell them if you think you have missed a dose or have been given too much medicine.
•The usual dose is 20 mg or 40 mg once a day.
•If you have severe liver problems, the maximum dose for GORD is 20 mg a day.
•The medicine will be given to you as a slow injection or infusion into one of your veins. The injection will be given over a period of at least 3 minutes, and the infusion over a period of 10 to 30 minutes.
•For prevention of re-bleeding gastric or duodenal ulcers, the usual dose is 80 mg administered as intravenous infusion over 30 minutes followed by a continuous infusion dose of 8 mg/hr given over 3 days. If you have severe liver problems for this indication, a continuous infusion dose of 4 mg/hr given over 3 days may be sufficient.
Children and adolescents
Esomeprazole should not be given to children or young people under the age of 18.
Elderly patients
No dose adjustment is necessary.
Handing instructions:
The reconstituted solution should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. Only clear solution should be used. The content of the vial is for single use only.
Injection
A solution for injection is prepared by adding 5 ml of 0.9% sodium chloride for intravenous use to the vial with esomeprazole.
When administering a 20 mg dose only half of the reconstituted solution should be used. Any unused solution should be discarded.
The reconstituted solution for injection is clear and colourless to very slightly yellow.
Infusion
A solution for infusion is prepared by dissolving the content of one vial with esomeprazole in up to 100 ml 0.9% sodium chloride for intravenous use.
The reconstituted solution for infusion is clear and colourless to very slightly yellow.
If you are given more Esomeprazole than you should be
Your doctor or nurse will always ensure that you receive the correct dose. If you are accidentally given an overdose you will be given the appropriate treatment.
If you have any further questions on the use of this product ask your doctor or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
If you notice any of the following rate but serious side effects, stop using and contact a doctor immediately:
•Sudden wheezing, swelling of your lips, tongue and throat or body, rash, fainting or difficulties to swallow (severe allergic reaction).
•Reddening of the skin with blisters or peeling. There may also be severe blisters and bleeding in the lips, eyes, mouth, nose and genitals. This could be ‘Stevens-Johnson syndrome’ or ‘toxic epidermal necrolysis’.
•Yellow skin, dark urine and tiredness which can be symptoms of liver problems.
These effects are rare, affecting less than 1 in 1,000 people.
Other side effects include:
Common (affects less than 1 in 10 people)
•Headache.
•Effects on your stomach or gut: diarrhoea, stomach pain, constipation, wind (flatulence).
•Feeling sick (nausea) or being sick (vomiting).
Uncommon (affects less than 1 in 100 people but more than 1 in 10)
•Swelling of the feet and ankles.
•Disturbed sleep (insomnia).
•Dizziness, tingling feelings such as “pins and needles”, feeling sleepy.
•Spinning feeling (vertigo).
•Eyesight problems such as blurred vision.
•Dry mouth.
•Changes in blood tests that check how the liver is working.
•Skin rash, lumpy rash (hives) and itchy skin.
Rare (affects less than 1 in 1,000 people but more than 1 in 100)
•Blood problems such as a reduced number of white cells or platelets. This can cause weakness, bruising or make infections more likely.
•Low levels of sodium in the blood. This may cause weakness, being sick (vomiting) and cramps.
•Feeling agitated, confused or depressed.
•Taste changes.
•Suddenly feeling wheezy or short of breath (bronchospasm).
•An inflammation of the inside of the mouth.
•An infection called “thrush” which can affect the gut and is caused by a fungus.
•Liver problems, including jaundice which can cause yellow skin, dark urine, and tiredness.
•Hair loss (alopecia).
•Skin rash on exposure to sunshine.
•Joint pains (arthralgia) or muscle pains (myalgia).
•Generally feeling unwell and lacking energy.
•Increased sweating.
Very rare (affects less than 1 in 10,000 people but more than 1 in 1,000)
•Changes in blood count including agranulocytosis (lack of white blood cells)
•Aggression.
•Seeing, feeling or hearing things that are not there (hallucinations).
•Severe liver problems leading to liver failure and inflammation of the brain.
•Sudden onset of a severe rash or blistering or peeling skin. This may be associated with a high fever and joint pains (Erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis).
•Muscle weakness.
•Severe kidney problems.
•Enlarged breasts in men.
•Low levels of magnesium in the blood. This may cause weakness, being sick (vomiting), cramps, tremor and arrhythmias (heart rhythm disturbances).
Not known (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data)
•Rash, possibly with pain in the joints.
If you are on Esomeprazole for more than three months it is possible that the levels of magnesium in your blood may fall.
INGREDIENTS
Contents of the pack and other information
What ESOMEZOL 40 contains
•Each vial of this medicine contains Esomeprazole (as sodium) 40mg as the active ingredient.
•The other ingredients are disodium edetate, sodium hydroxide for pH adjustment.
What ESOMEZOL 40 looks like and contents of the pack
ESOMEZOL 40 is a white or almost white lyophilized powder which comes in a clear glass vial fitted with a rubber cap and metal seal.
The pack contains a vial containing 40 mg esomeprazole, also contains an ampoule containing 5 ml 0.9% sodium chloride injections.
STORE
How to store ESOMEZOL 40
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
Do not use after the expiry date ‘EXP’ shown on the container. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
Store below 25°C. Protect from light.
Once the medicine has been mixed with provided solvent, the solution should be used straight away. Any unused liquid should be disposed of safely.