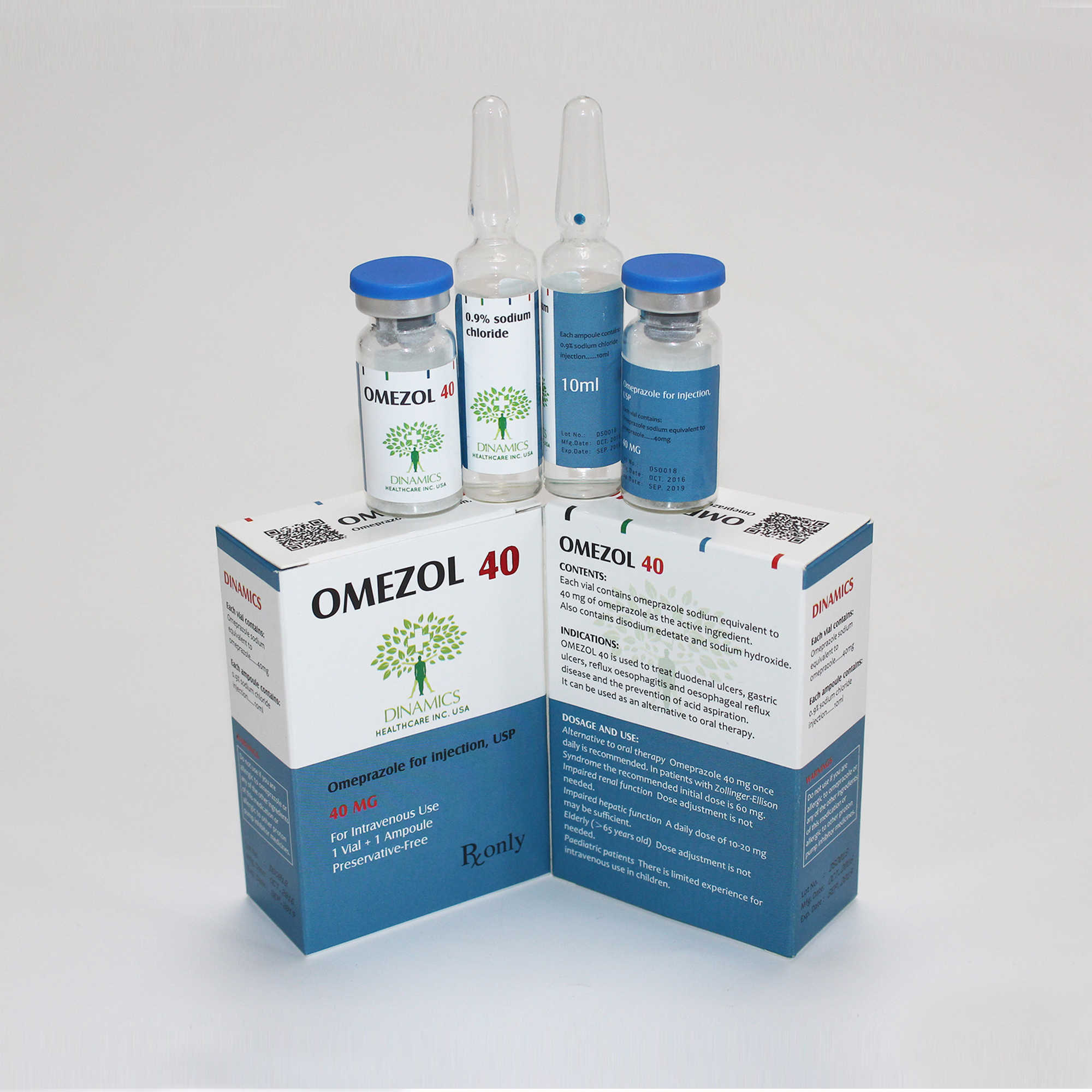
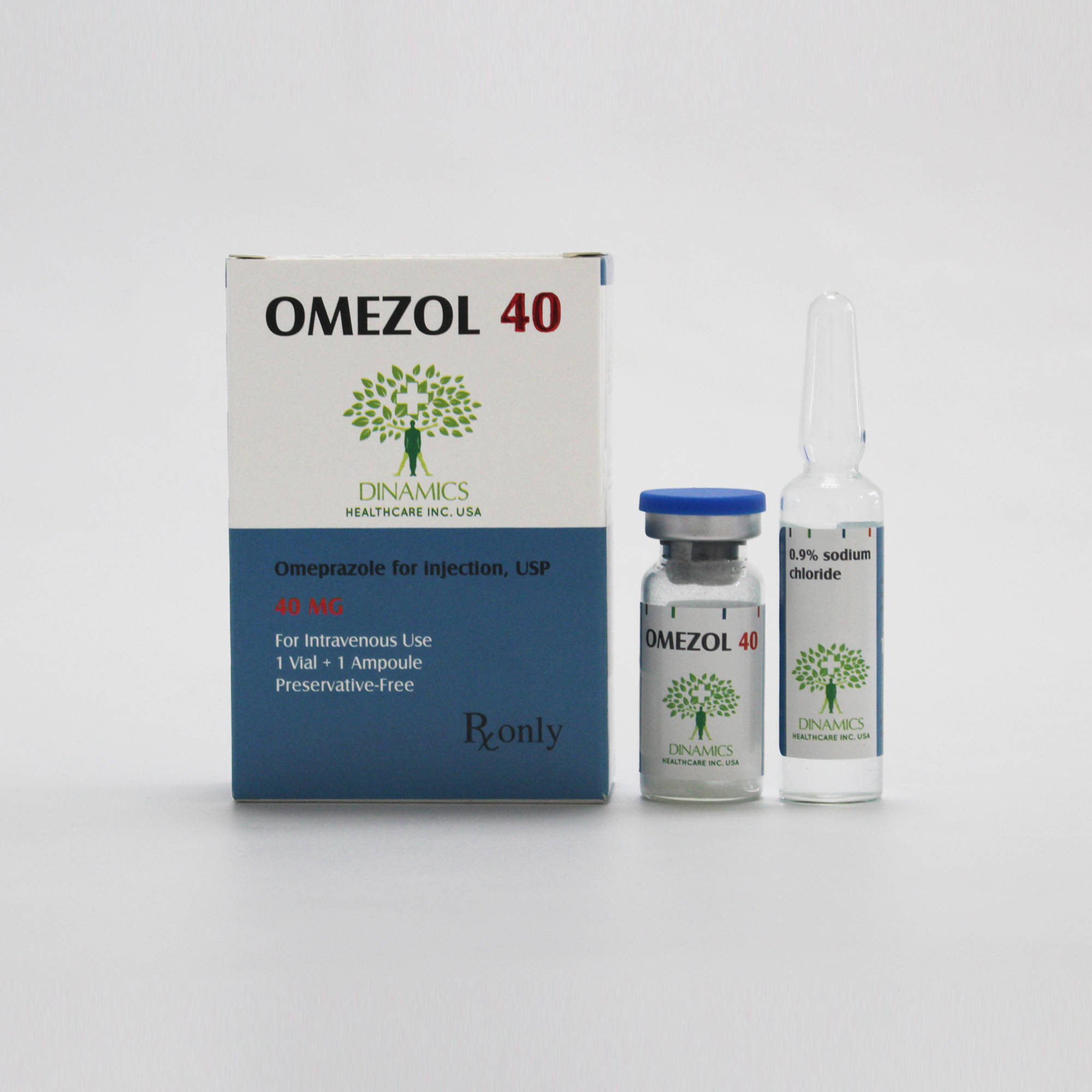
1.How to take OMEZOL 40
•Omeprazole can be given to adults including the elderly.
•There is limited experience with Omeprazole for intravenous use in children.
Being given OMEZOL 40
• It will be given to you by a doctor or nurse who will decide how much you need. •The medicine will be given to you as an injection or infusion into one of your veins.
Dosage
Alternative to oral therapy
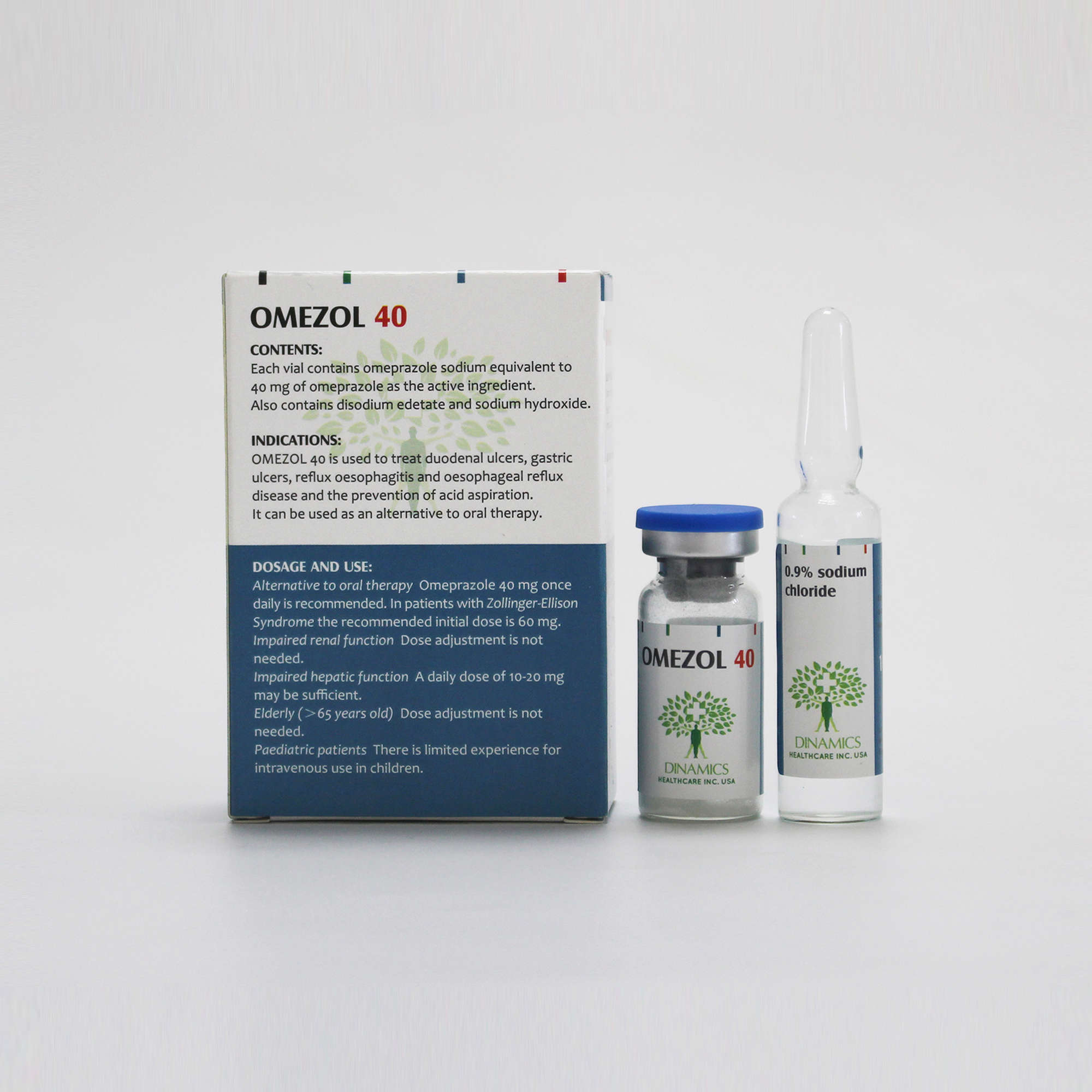
In patients with duodenal ulcer, gastric ulcer or reflux oesophagitis where oral medication is inappropriate, 40 mg once daily is recommended. In patients with Zollinger-Ellison syndrome the recommended initial dose given intravenously is 60 mg daily. Higher daily doses may be required and the dose should be adjusted individually. When doses exceed 60 mg daily, the dose should be divided and given twice daily.
Special populations
Impaired Renal Function
Dose adjustment is not needed in patients with impaired renal function.
Impaired Hepatic Function
As plasma half-life of omeprazole is increased in patients with impaired hepatic function a daily dose of 10 - 20 mg may be sufficient.
Elderly (> 65 years old)
Dose adjustment is not needed in the elderly.
Paediatric patients
There is limited experience with Omeprazole for intravenous use in children.
Method of Administration
Intravenous Injection
OMEZOL 40 can be given as a slow intravenous injection. The solution for IV injection is obtained by adding to the vial of the solvent provided. Discoloration may occur if incorrect reconstitution technique is used. After reconstitution the injection should be given slowly over a period of at least 3 minutes. The solution should be used within 4 hours of reconstitution.
Intravenous Infusion
OMEZOL 40 can be given as an intravenous infusion (over a period of 20-30 minutes or more). The contents of one vial must be dissolved in 100 mL saline for infusion or 100 mL 5% dextrose for infusion. The solution should be used within 12 hours when omeprazole is dissolved in saline and within 6 hours when dissolved in 5% dextrose. After reconstitution, start the infusion immediately. The constituted solution should not be mixed or co-administered in the same infusion set with any other drug.
If you are given more OMEZOL 40 than you should
If you think you have been given too much Omeprazole, talk to your doctor straight away.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
If you notice any of the following rate but serious side effects, stop using and contact a doctor immediately:
•Sudden wheezing, swelling of your lips, tongue and throat or body, rash, fainting or difficulties to swallow (severe allergic reaction).
•Reddening of the skin with blisters or peeling. There may also be severe blisters and bleeding in the lips, eyes, mouth, nose and genitals. This could be 'Stevens-Johnson syndrome' or 'toxic epidermal necrolysis'.
•Yellow skin, dark urine and tiredness which can be symptoms of liver problems.
Side effects may occur with certain frequencies, which are defined as follows: Very common: affects more than 1 user in 10
Common: affects 1 to 10 users in 100
Uncommon: affects 1 to 10 users in 1,000
Rare: affects 1 to 10 users in 10,000
Very rare: affects less than 1 user in 10,000
Not known: frequency cannot be estimated from the available data.
Other side effects include:
Common side effects
•Headache.
•Effects on your stomach or gut: diarrhoea, stomach pain, constipation, wind (flatulence).
•Feeling sick (nausea) or being sick (vomiting).
Uncommon side effects
•Swelling of the feet and ankles.
•Disturbed sleep (insomnia).
•Dizziness, tingling feelings such as “pins and needles”, feeling sleepy.
•Spinning feeling (vertigo).
•Changes in blood tests that check how the liver is working.
•Skin rash, lumpy rash (hives) and itchy skin.
•Generally feeling unwell and lacking energy.
Rare side effects
•Blood problems such as a reduced number of white cells or platelets. This can cause weakness, bruising or make infections more likely.
•Allergic reactions, sometimes very severe, including swelling of the lips, tongue and throat, fever, wheezing.
•Low levels of sodium in the blood. This may cause weakness, being sick (vomiting) and cramps.
•Feeling agitated, confused or depressed.
•Taste changes.
•Eyesight problems such as blurred vision.
•Suddenly feeling wheezy or short of breath (bronchospasm).
•Dry mouth.
•An inflammation of the inside of the mouth.
•An infection called “thrush” which can affect the gut and is caused by a fungus.
•Liver problems, including jaundice which can cause yellow skin, dark urine, and tiredness.
•Hair loss (alopecia).
•Skin rash on exposure to sunshine.
•Joint pains (arthralgia) or muscle pains (myalgia). •Severe kidney problems (interstitial nephritis).
•Increased sweating. Very rare side effects
•Changes in blood count including agranulocytosis (lack of white blood cells).
•Aggression.
•Seeing, feeling or hearing things that are not there (hallucinations).
•Severe liver problems leading to liver failure and inflammation of the brain.
•Sudden onset of a severe rash or blistering or peeling skin. This may be associated with a high fever and joint pains (Erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis).
•Muscle weakness.
•Enlarged breasts in men.Go to top of the page